- Lithosphere Facts For Kids
- Lithosphere Geography Definition
- Definition Of Lithosphere Geography Earth
- Lithosphere Geography Definition
ADVERTISEMENTS:
- The lithosphere is the solid, outer part of the Earth. The lithosphere includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust, the outermost layers of Earth’s structure.
- Play this game to review Geography. What layer of the earth is made of liquid magma?
- Asthenosphere, zone of Earth’s mantle lying beneath the lithosphere and believed to be much hotter and more fluid than the lithosphere. The asthenosphere extends from about 100 km (60 miles) to about 700 km (450 miles) below Earth’s surface.
Lithosphere Essay – This is one of the best essays on ‘Lithosphere’ especially written for school and college students.
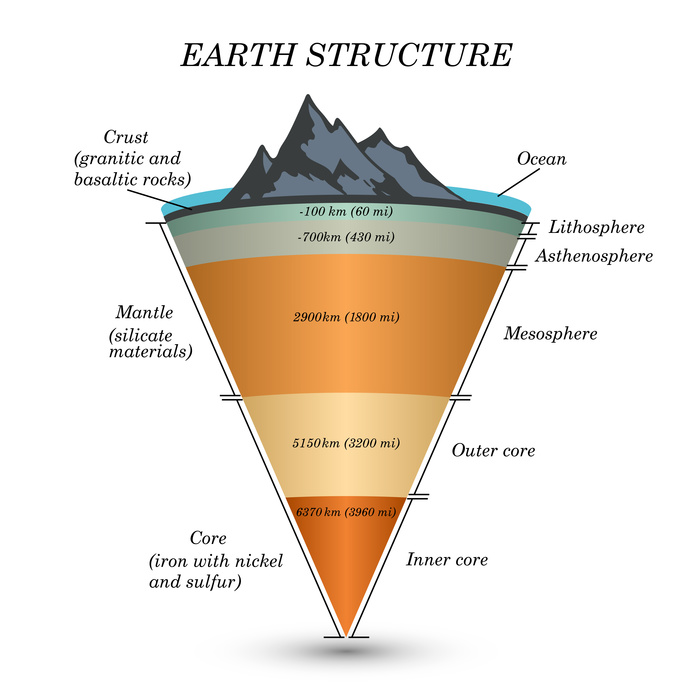
The planet Earth comprises several layers. Starting from the Earth’s surface, there are four main layers; namely, the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. The pressure and temperature increases tremendously from the outer layers to the inner layers. Let’s take a look at each of them individually.
The melting of mantle material that occurs when the material rises into a region of lower pressure, allowing it to cross from its solidus to its liquidus. Decompression melting takes place in mantle plumes and regions where plate movements stretch the crustal rocks, making them thinner.
The lithosphere, Greek for “rocky sphere,” is the outermost shell of the Earth. The term is also used to refer to the outermost rocky shell of other solid planets. It is a relatively thin layer, 50-100 km thick under the oceans, 150 km thick on the continents. The lithosphere is composed of the upper crust, 5 km thick in the oceans and 65 km thick on the continents, and the upper mantle, which makes up the remainder.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
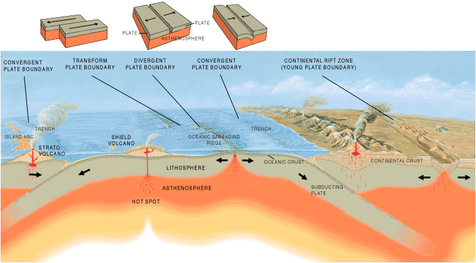
Separating the crust and the upper mantle is the Mohorovicic discontinuity, the point at which rocks become plastic rather than solid. Beneath the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, which continues the upper mantle, and is approximately the point at which the mantle becomes liquid. In the Earth, the lithosphere includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, which constitute the hard and rigid outer layer of the Earth.
The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere, the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The boundary between the lithosphere and the underlying asthenosphere is defined by a difference in response to stress the lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plastic deformation.
The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates.
It is made of following four layers:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
i. The Crust:
The crust or the lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth made up of silicate rock materials. The crust makes up only about one percent of the Earth and is the thinnest layer in comparison to the other three layers. Most earthquakes occur in the Earth’s crust. The thickness and the composition of the Earth’s crust vary in the land and the ocean. For example, the continental crust is about 32 kilometer thick and composed of lighter materials like granite, quartz and feldspar; whereas, the oceanic crust measures about 10 kilometers and is mostly made up of basalt.
ii. The Mantle:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The mantle, the largest layer of the Earth, is made up of iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, silicone and oxygen. In fact, most of the Earth’s mass (about 80 percent) lies in the mantle. The temperature in this layer is estimated to be about 1000 degrees Celsius. It is in this layer that volcano magma is present. For better understanding, we can say that the mantle layer is divided into the upper and lower sections. The upper mantle is much cooler than the lower (deeper) section. The overall thickness of the mantle layer is 2900 kilometers.
Lithosphere Facts For Kids
iii. The Outer Core:
Lithosphere Geography Definition
The outer core can be regarded as a ball of very hot metals. The outer core is liquid and made up of iron and nickel. The density is very high, but less than pure molten iron. Hence, scientists are of the opinion that sulfur and oxygen may be present in the outer core. (This is due to the fact that they dissolve easily in liquid iron.) The outer core measures 2200 kilometers in thickness. As the Earth rotates, the outer core (consisting of iron) spins over the inner core and generates the Earth’s magnetic field, which is the factor responsible for functioning of the magnetic compass.

iv. The Inner Core:
Definition Of Lithosphere Geography Earth
Tire inner core, as the name suggests, is the innermost layer of the Earth, and is characterized by extremely high temperature and pressure conditions. The temperature of the inner core layer is more than the sun’s surface. The intense heat reflected from the inner core mobilizes the materials of the outer core and the mantle. It is due to the high pressure that the inner core materials are unable to move, and hence remain solid. The thickness of the inner core is believed to be about 1250 kilometers.
Lithosphere Geography Definition
The diameter of the Earth is 12,756 kilometers. The Earth is enveloped by atmosphere, which comprises four major layers, namely, the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. The atmosphere provides air, water, warmth and protects from the harmful rays of the sun. Without atmosphere, life on earth would be impossible!